Biotech firms: Health innovation can’t grow in KC with wet lab space in such short supply
July 25, 2019 | Rashi Shrivastava
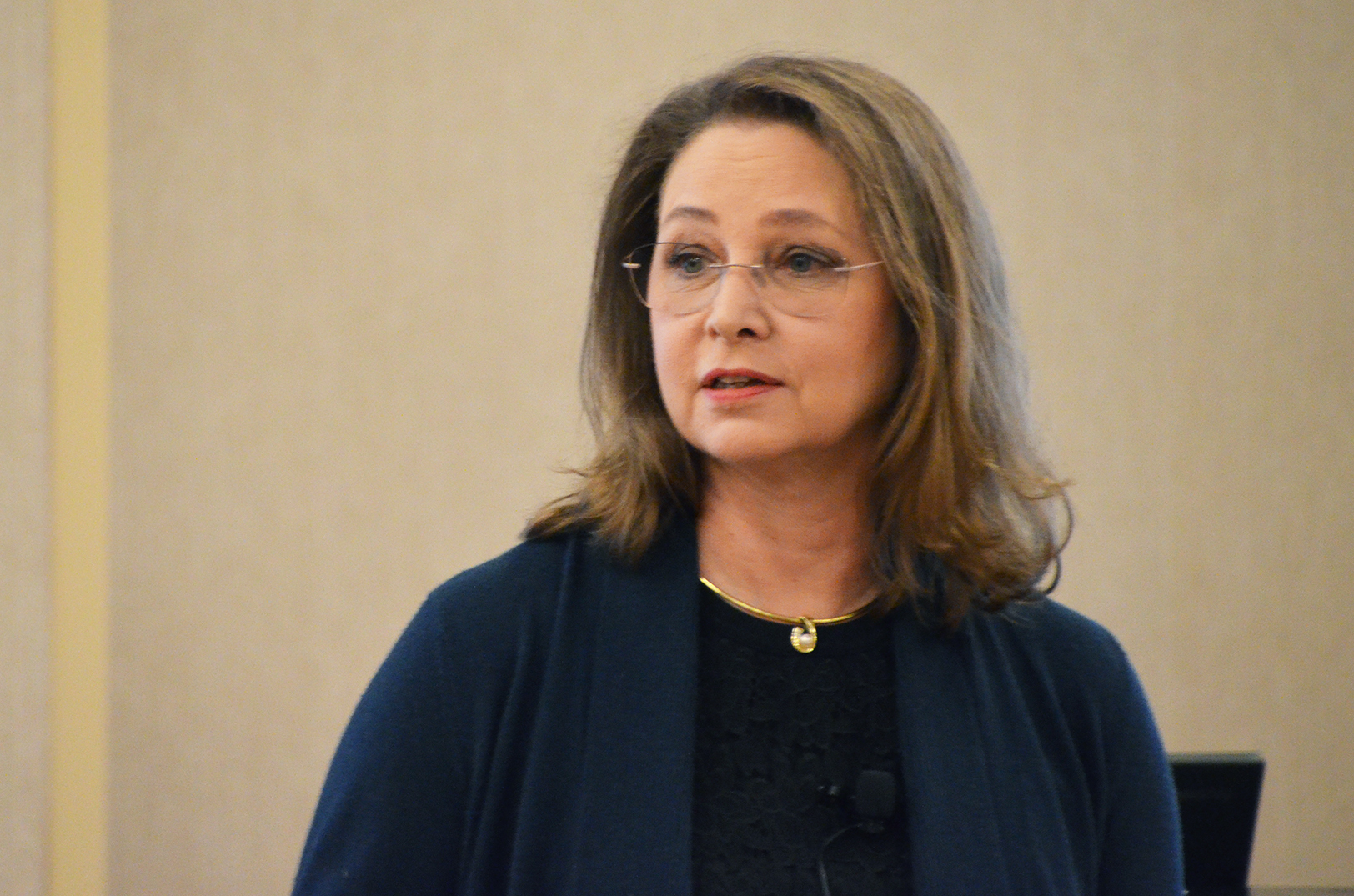

ELIAS Animal Health is advancing a technology that can fundamentally change how cancer is treated in both humans and animals, said CEO Tammie Wahaus, yet finding lab space in the metro has been one of the biotech startup’s biggest tests.
“We’re doing a lot of cell culture work, which requires wet lab space, but there are a limited number of incubator or accelerator facilities that provide it,” she said of the struggles that bubbled up five years ago when ELIAS Animal Health was created as a spin-off of parent company TVAX Biomedical Inc.
Instead of sporting desks and chairs, wet labs are equipped with paraphernalia like sterilisation equipment, freezers, centrifuges and have access to water, all of which are essential to conduct clinical trials, explained Wahaus.
Sharing equipment out of communal wet lab spaces offers flexibility, which can be especially fruitful for a company in its pilot stage, she said.
“As a startup company, when you’re in the early stages of development, you might only need 750 square feet of lab space. What’s beneficial about venture accelerators is that when you need to double your space, you simply rent another lab,” said Wahaus.
Since 2016, ELIAS Animal Health has been leasing two labs and two offices in the Kansas Bioscience Park Venture Accelerator in Olathe, she said. The company sealed the deal only after realising that the equipment at other wet lab locations was dated and not suited for cell manufacturing.
“Most wet lab spaces are actually equipped for chemo therapeutics, but cell-based manufacturing is more prevalent today than it was when most of these were designed and so they have the wrong equipment,” said Wahaus.
‘Gorilla in the room’
High in demand and low in supply, wet labs in the city are mostly at full capacity, said Dennis Ridenour, president and CEO of BioNexus KC, an organization that aims to optimize resources for entrepreneurs developing life sciences technology in the region.
“Different types of companies need different types of equipment, so it’s expensive to make a lab space that is relevant to everybody,” Ridenour said.
Lack of access to capital and talent makes the need for affordable and accessible lab space even more dire for biotech startups, he said.
“The gorilla in the room is that for the last several years there has been a lack of funding. We still see a lack of proof of concept and seed stage funding when the research funding is drying up, but the technology is too early to be of interest to angel investors,” said Ridenour.
Investments meet talent
Tony Simpson, a business development consultant with TechAccel attributes it to the nature of biotech firms that tend to need more money and more time. TechAccel is a venture that identifies and invests in animal health and agtech firms to further develop their technologies.
“Smart capital is very important, which means having folks that can not only provide capital, but also understand the space, can be educated about the plan,” Simpson said.
Though the fruition of their technologies can take awhile, biotech startups have huge market opportunities and can grow extremely fast, said Ridenour.
“I could see a way forward for corporate partnerships where large employers could set up these types of accelerators with wet lab spaces,” he said.
Creating more wet lab spaces can not only create high-paying professional jobs, but also job openings for those without degrees, said Brad Fabbri, chief scientific officer at TechAccel.
“If a region wants to be competitive in attracting innovative entrepreneurial companies, there really needs to be an investment in incubator spaces, that would have let wet lab space,” Fabbri said.
TechAccel works closely with the founders to help them commercialize technologies created out of academia, Simpson said. By funneling support through funding, technical guidance and industry insights, the venture helps biotech startups reach their potential, he said.
“It’s not just space in labs, it’s access to talent, mentors, and capital,” said Simpson. “It’s really about how do we build an ecosystem or a community to really drive entrepreneurship and create a broader community upon which these companies can grow and become successful?”
This story was produced through a collaboration between Missouri Business Alert and Startland News.
Featured Business

2019 Startups to Watch
stats here
Related Posts on Startland News
Digital Sandbox taps K-State Olathe for office space
The partnership between Digital Sandbox KC and the City of Olathe, Kan. is now a bit stronger. Companies funded out of the Olathe program will now have access to an office and coworking space via the Kansas State University Olathe campus, located at 22201 W. Innovation Dr., Olathe, Kansas. “We’re constantly working to break down…
A coworking studio for artists, InterUrban ArtHouse to open in Overland Park
A new coworking and community space for artists is coming to the Kansas City area. Scheduled to open June 15 in Overland Park, the nearly 10,000 square-foot InterUrban ArtHouse is revamping a post office to become a shared space for 20 to 40 artists. The nonprofit is piggybacking on a popular trend in the metro…
Athlete Network adds hall-of-famer Warren Moon to its roster
It’s not everyday that you add a hall-of-fame quarterback to your team. In establishing a new, high-impact advisory board, Athlete Network has landed former NFL superstar Warren Moon as a team member that will help guide the startup moving forward. Moon previously played for the Houston Oilers, Minnesota Vikings and other pro teams, racking up…
2017 Sprint Accelerator class makes its KC introductions at 1 Million Cups
Less than two weeks into the program, the 2017 Sprint Accelerator cohort introduced themselves to the community on Wednesday at 1 Million Cups. The accelerator recently welcomed seven startups representing its two tracks — ag tech and digital — that arrives from all around the country. Hailing from states like Texas, New York, Florida, Georgia…