Sickweather forecasts flu trouble ahead, urges handwashing and vaccinations
October 15, 2018 | Elyssa Bezner
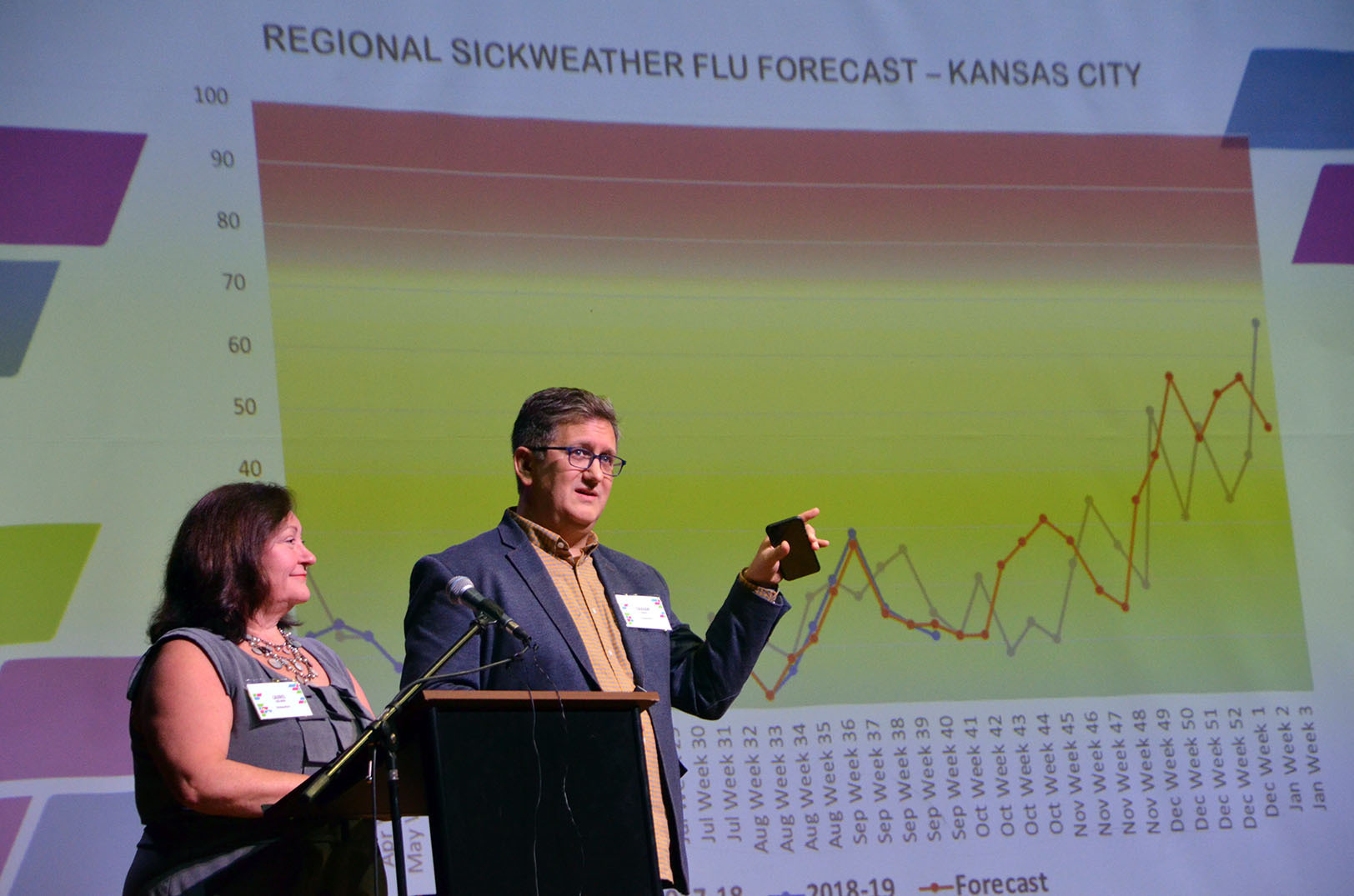
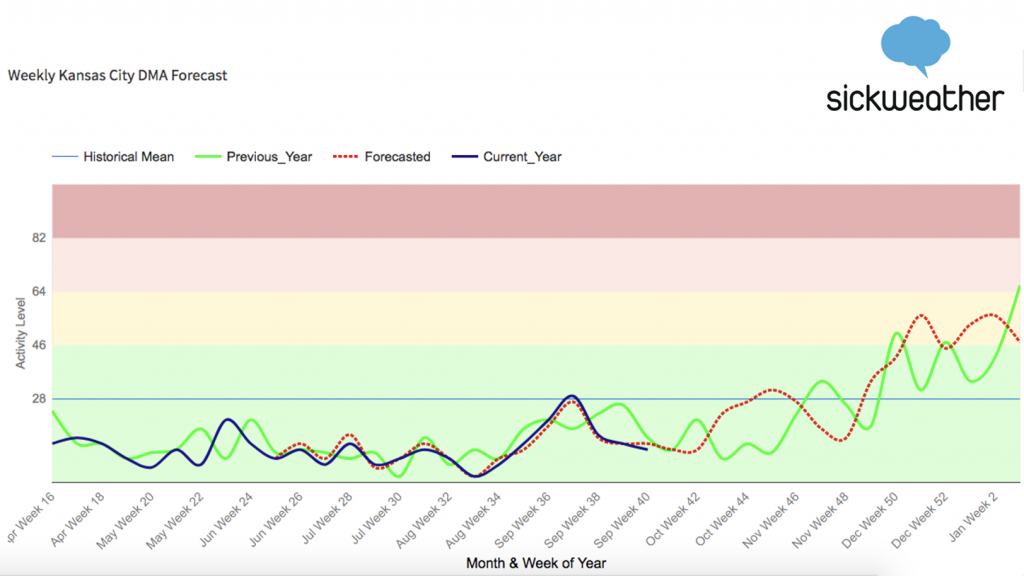
Sickweather’s illness forecasting technology points to a seasonal uptick in influenza rates for Kansas City, said Laurel Edelman, noting a particularly rough patch expected at the end of year.
“We actually see more of a dome here in Kansas City,” said Edelman, the chief revenue officer for Sickweather, referring to a chart that plots expected flu rates through early 2019. “So you’re going to see a longer period of time of higher illness for the last two weeks of December, and the first two weeks of January.”
The app-based illness forecaster — founded in Baltimore in 2010, but now headquartered in Kansas City — played host Monday to its first Sickweather Cold Cough Flu conference in the Medallion Theater at Plexpod Westport Commons. The event, which also marked Global Handwashing Day, opened with a press conference detailing the firm’s local, regional and national predictions for the coming flu season.
Sickweather’s projections in 2017-2018 strongly correlated to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control’s reports on the previous season, Edelman said, noting a 90-percent accuracy rate for the app’s technology. It’s success has reversed her former attitude that influenza could not be predicted, she said.
“The challenge is to engage you to help you to understand what we’re trying to do,” Edelman said. “And how we’re trying to move forward with this whole concept of forecasting a disease that for many, many years I told everyone could not be forecast.”
“This is a virus. It’s live. It changes,” she said.
Approaches to and attitudes about the flu virus, as well as other diseases, have changed in a way that concerns her, Edelman added.
“Some of them are fantastic in terms of people being aware and knowledgeable, and others, in my personal opinion, are at times troubling,” she said. “An example of that is that the number of parents who don’t vaccinate their children for any disease has quadrupled since 2011.”
Sickweather’s forecast is intended to help build actionable information that could help change that trend, she said.
“This means that there’s still a heck of a long opportunity to vaccinate. If we assume and understand that vaccination becomes effective between seven to 14 days from when you’re vaccinated, now’s the time to be vaccinated,” said Edelman. “You’re vaccinating not just yourself, but you’re also helping to keep your germs away from people who can’t get vaccinated.”
Featured Business

2018 Startups to Watch
stats here
Related Posts on Startland News
Events Preview: Conquer for Good, TEDxUMKC
There are a plethora of entrepreneurial events hosted in Kansas City on a weekly basis. Whether you’re an entrepreneur, investor, supporter, or curious community member — we recommend these upcoming events for you. Are you hosting a relevant community event? Feel free to add it to the FWD/KC calendar for increased exposure. Once your event…
Jaguar Land Rover invests in artificial intelligence startup Mycroft
Mycroft has received a significant boost in horsepower. Only a few weeks after entering 500 Startups, Mycroft has landed a strategic partnership with Jaguar Land Rover. The Kansas City-based artificial intelligence startup is among the first startups to enter the Portland-based Jaguar Land Rover Tech Incubator, which will provide Mycroft with a $110,000 investment and…
KC-based OYO Fitness closes a historically successful Kickstarter
To say that OYO Fitness has a successful Kickstarter campaign would be an understatement. The Kansas City-based fitness firm folded up and then crushed its recent crowdfunding effort, which raised a stunning $659,000 for its collapsible and compact exercise device. OYO’s DoubleFlex Black campaign — which snagged pre-orders from 4,200 backers — was the second…
Survivor, innovator Kim Gandy rewards patients for sticking to treatments
In her 20 years working as a transplantation clinician, Kim Gandy found it baffling that a seemingly simple problem had such a difficult time finding a solution. Transplant patients consistently struggled to adhere to their health regimens, resulting not only in significant costs for care providers but also death. “We were literally losing patients,” Gandy…